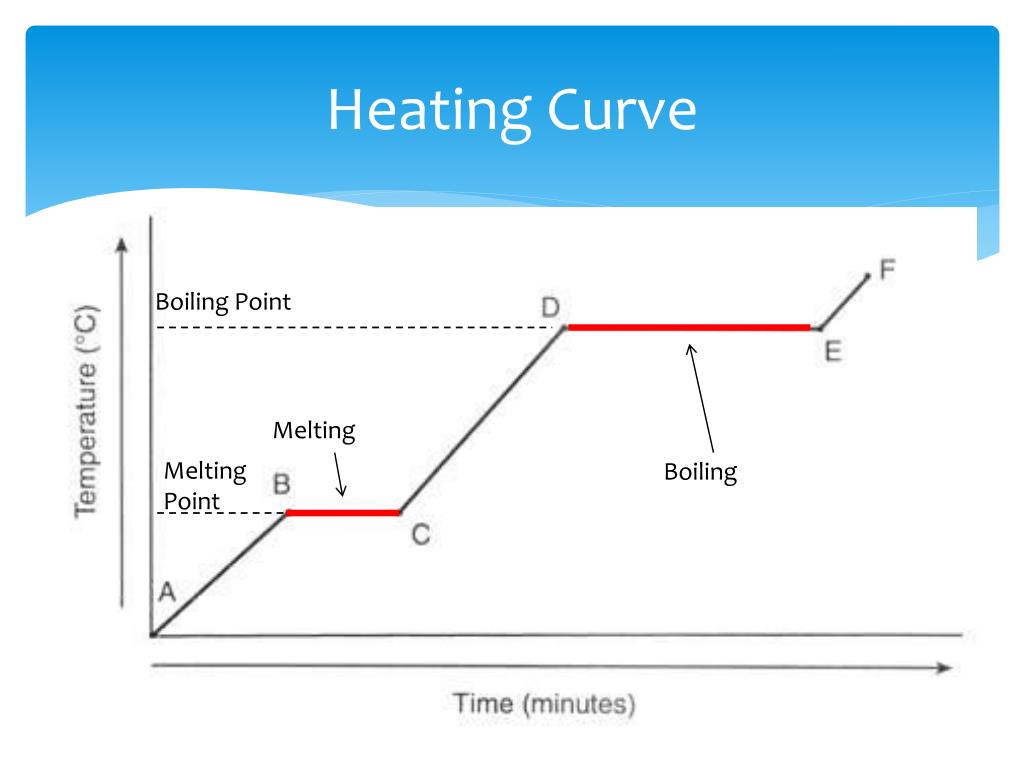
Heating Curve Liquid . The heating curve for water shows how the temperature of a given quantity of water changes. Heating and cooling curves are graphs. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat energy. Heating curves provide valuable information about the thermal properties of substances, including their specific heat capacities, latent heats of. The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. Plots of the temperature of a substance versus heat added or versus heating time at a constant rate of heating are called heating curves. A heating curve shows how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up at a constant rate. This plot of temperature shows what happens to a 75 g sample of ice initially at 1 atm and −23°c as heat is added at a constant rate:
from www.slideserve.com
Heating curves provide valuable information about the thermal properties of substances, including their specific heat capacities, latent heats of. When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. A heating curve shows how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up at a constant rate. Heating and cooling curves are graphs. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat energy. This plot of temperature shows what happens to a 75 g sample of ice initially at 1 atm and −23°c as heat is added at a constant rate: The heating curve for water shows how the temperature of a given quantity of water changes. The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). Plots of the temperature of a substance versus heat added or versus heating time at a constant rate of heating are called heating curves.
PPT Thermal Properties of Matter (Part I) PowerPoint Presentation
Heating Curve Liquid Heating and cooling curves are graphs. A heating curve shows how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up at a constant rate. When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). Plots of the temperature of a substance versus heat added or versus heating time at a constant rate of heating are called heating curves. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat energy. The heating curve for water shows how the temperature of a given quantity of water changes. This plot of temperature shows what happens to a 75 g sample of ice initially at 1 atm and −23°c as heat is added at a constant rate: Heating curves provide valuable information about the thermal properties of substances, including their specific heat capacities, latent heats of. Heating and cooling curves are graphs.
From wisc.pb.unizin.org
M6Q6 Calorimetry continued Phase Changes and Heating Curves Chem Heating Curve Liquid The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). The heating curve for water shows how the temperature of a given quantity of water changes. When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat energy. A heating curve shows how. Heating Curve Liquid.
From study.com
Heating & Cooling Curves Definition, Phases & Examples Lesson Heating Curve Liquid The heating curve for water shows how the temperature of a given quantity of water changes. Plots of the temperature of a substance versus heat added or versus heating time at a constant rate of heating are called heating curves. A heating curve shows how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up at a constant rate. The heat. Heating Curve Liquid.
From allisonrswankxo.blob.core.windows.net
Heating Cooling Curve Of Water Heating Curve Liquid Heating curves provide valuable information about the thermal properties of substances, including their specific heat capacities, latent heats of. When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). A heating curve shows how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up. Heating Curve Liquid.
From www.studyblue.com
Chapter 15 Properties of Solids at Yavapai College StudyBlue Heating Curve Liquid For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat energy. The heating curve for water shows how the temperature of a given quantity of water changes. A heating curve shows how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up at a constant rate. Heating curves provide valuable information about the thermal properties of substances, including their specific. Heating Curve Liquid.
From www.youtube.com
Heating and Cooling Curve / Introduction plus and Potential Heating Curve Liquid A heating curve shows how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up at a constant rate. This plot of temperature shows what happens to a 75 g sample of ice initially at 1 atm and −23°c as heat is added at a constant rate: The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ. Heating Curve Liquid.
From www.researchgate.net
15 Schematic cooling (1) and heating (2) DSC curves, showing a range of Heating Curve Liquid Heating and cooling curves are graphs. The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat energy. When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. Plots of the temperature of a substance versus heat added or versus heating time at. Heating Curve Liquid.
From spmphysics.onlinetuition.com.my
The Heating Curve SPM Physics Form 4/Form 5 Revision Notes Heating Curve Liquid Heating curves provide valuable information about the thermal properties of substances, including their specific heat capacities, latent heats of. When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. Heating and cooling curves are graphs. Plots of the temperature of a substance versus heat added or versus heating time at a constant rate of heating are called heating curves.. Heating Curve Liquid.
From chem.libretexts.org
11.7 Heating Curve for Water Chemistry LibreTexts Heating Curve Liquid Plots of the temperature of a substance versus heat added or versus heating time at a constant rate of heating are called heating curves. Heating curves provide valuable information about the thermal properties of substances, including their specific heat capacities, latent heats of. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat energy. A heating curve shows how. Heating Curve Liquid.
From www.coursehero.com
[Solved] Given below is the graph of a substance's heating curve Heating Curve Liquid When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. Plots of the temperature of a substance versus heat added or versus heating time at a constant rate of heating are called heating curves. This plot of temperature shows what happens to a 75 g sample of ice initially at 1 atm and −23°c as heat is added at. Heating Curve Liquid.
From brainly.in
To study the effect of heat on ice by using a graph Brainly.in Heating Curve Liquid Plots of the temperature of a substance versus heat added or versus heating time at a constant rate of heating are called heating curves. The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). This plot of temperature shows what happens to a 75 g sample of ice initially at 1 atm and −23°c. Heating Curve Liquid.
From www.worldwisetutoring.com
Heating and Cooling Curves Heating Curve Liquid The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). Heating and cooling curves are graphs. When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. Plots of the temperature of a substance versus heat added or versus heating time at a constant rate of heating are called heating curves. This plot of. Heating Curve Liquid.
From quizizz.com
Heating and Cooling Curves Chemistry Quiz Quizizz Heating Curve Liquid When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. A heating curve shows how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up at a constant rate. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat energy. This plot of temperature shows what happens to a 75 g sample of ice initially at 1 atm and. Heating Curve Liquid.
From app.jove.com
Heating and Cooling Curves Concept Chemistry JoVe Heating Curve Liquid When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). Plots of the temperature of a substance versus heat added or versus heating time at a constant rate of heating are called heating curves. Heating and cooling curves are graphs. A heating curve. Heating Curve Liquid.
From study.com
Phase Changes and Heating Curves Video & Lesson Transcript Heating Curve Liquid The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. For heating curves, we start with a solid and add heat energy. The heating curve for water shows how the temperature of a given quantity of water changes. A heating curve shows how. Heating Curve Liquid.
From askfilo.com
The graph below shows the heating curve for a pure substance. The tempera.. Heating Curve Liquid A heating curve shows how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up at a constant rate. Heating and cooling curves are graphs. Heating curves provide valuable information about the thermal properties of substances, including their specific heat capacities, latent heats of. When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. This plot of temperature shows what. Heating Curve Liquid.
From studylib.net
UNIT 2 LESSON 9 Heating Curve and Cooling Heating Curve Liquid When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. Plots of the temperature of a substance versus heat added or versus heating time at a constant rate of heating are called heating curves. The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). The heating curve for water shows how the temperature. Heating Curve Liquid.
From www.smartexamresources.com
IGCSE Chemistry Notes Solids, Liquids And Gases Smart Exam Resources Heating Curve Liquid The heating curve for water shows how the temperature of a given quantity of water changes. The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. Heating and cooling curves are graphs. This plot of temperature shows what happens to a 75 g. Heating Curve Liquid.
From brainly.in
Q2. The given graph shows the heating curve for a pure substance,the Heating Curve Liquid When the liquid reaches its boiling point, the liquid begins to. The heat absorbed depends on the liquid's heat capacity ( q = mcliquid δ t ). Heating curves provide valuable information about the thermal properties of substances, including their specific heat capacities, latent heats of. A heating curve shows how the temperature changes as a substance is heated up. Heating Curve Liquid.